Retinal Diseases: What Every Diabetic Should Know About Vision Loss
Retinal Diseases: What Every Diabetic Should Know About Vision Loss

Retinal Diseases: What Every Diabetic Should Know About Vision Loss
Diabetes affects nearly every organ in the body, but its impact on the eyes is often underestimated. Retinal disease is one of the most serious complications of diabetes and a leading cause of vision loss among adults in the UAE. What makes diabetic retinal disease especially concerning is that it progresses silently. Many individuals notice no symptoms until significant damage has already occurred. Understanding how diabetes affects the retina and why annual screenings are essential can save vision and prevent long-term disability.
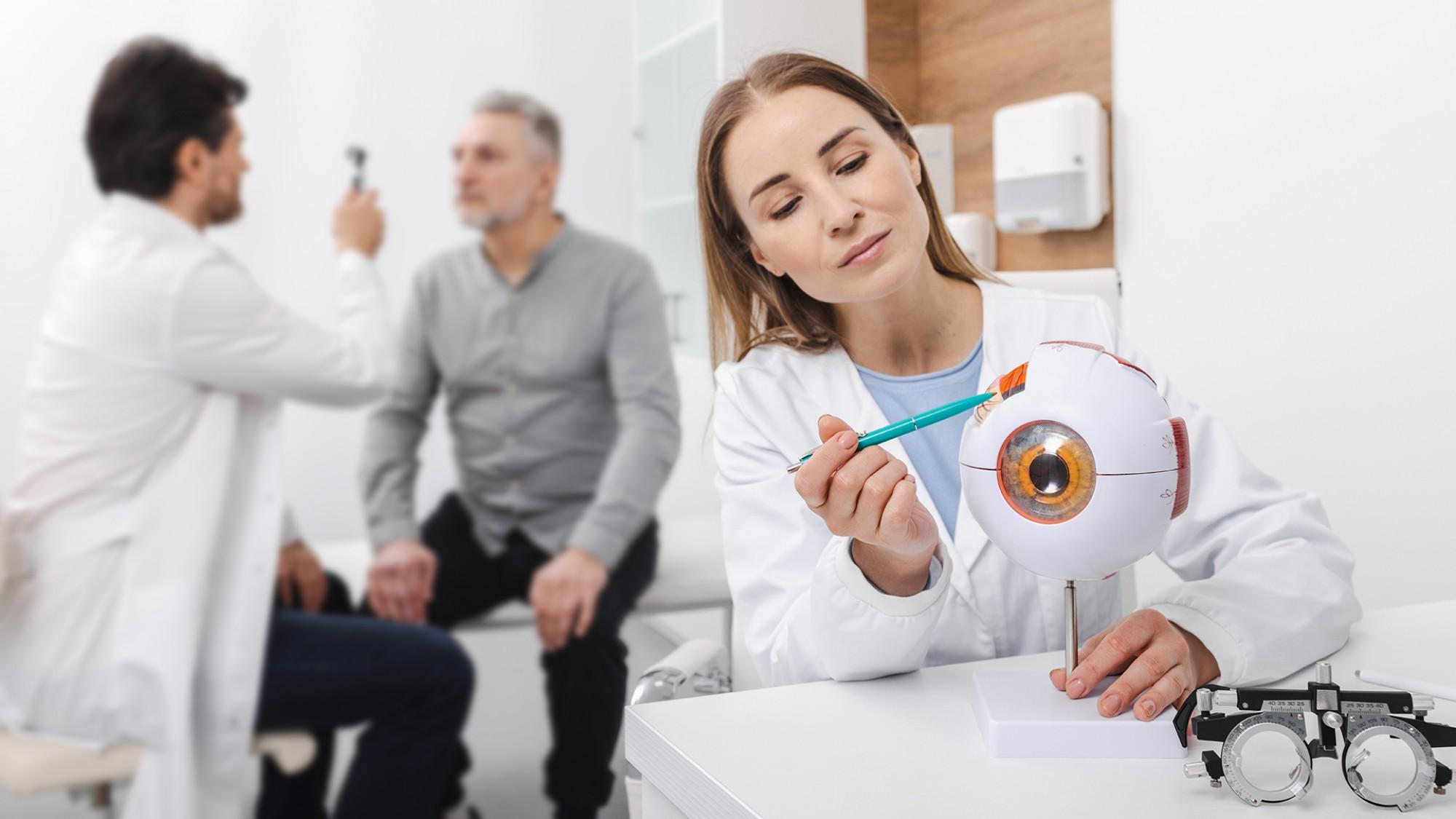
The retina is a delicate layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye. It is responsible for capturing light and sending signals to the brain. High blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy. Over time, vessels may leak fluid, swell, or close off completely. The retina may respond by growing fragile new vessels that break easily and bleed.
The earliest stage, non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), often has no symptoms. Yet subtle changes are already occurring—microaneurysms, small hemorrhages, and areas of poor blood flow. Without monitoring, this can advance to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), where abnormal new vessels form. These vessels can bleed into the eye, causing sudden vision loss or retinal detachment.
Another serious complication is diabetic macular edema (DME). The macula, responsible for sharp central vision, becomes swollen due to fluid leakage. Patients may notice blurry or distorted vision, but in many cases, the swelling begins silently. This is why diabetes specialists and ophthalmologists emphasize imaging tests even when the patient reports no symptoms.
Annual retinal exams are essential for all individuals with diabetes. In Dubai, advanced imaging technologies—such as OCT scans and wide-field retinal photography—allow early detection of even microscopic changes. These tools reveal swelling, vessel abnormalities, and early ischemia long before visual symptoms begin.
Timely treatment dramatically improves outcomes. Anti-VEGF injections help control swelling and prevent harmful vessel growth. Laser therapy can seal leaking areas or strengthen weak vessels. In advanced cases, vitrectomy surgery may be required to remove blood or scar tissue. With proper management, many patients maintain stable vision for years.
Lifestyle factors also play an essential role. Stable blood sugar levels, controlled blood pressure, a healthy diet, physical activity, and smoking cessation all reduce the risk of retinal damage. During Ramadan, individuals with diabetes should work closely with their doctors to adjust medication and dietary habits to maintain consistent sugar control, protecting the eyes throughout the fasting period.
Retinal disease may be silent, but it is not inevitable. With annual screenings, early diagnosis, and proper management, diabetics in the UAE can protect their sight and maintain a high quality of life. The key is simple: never wait for symptoms—your eyes deserve proactive care.





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









