Autoimmune Disorders Explained: From Rheumatoid Arthritis to Lupus
Autoimmune Disorders Explained: From Rheumatoid Arthritis to Lupus
Autoimmune Disorders Explained: From Rheumatoid Arthritis to Lupus
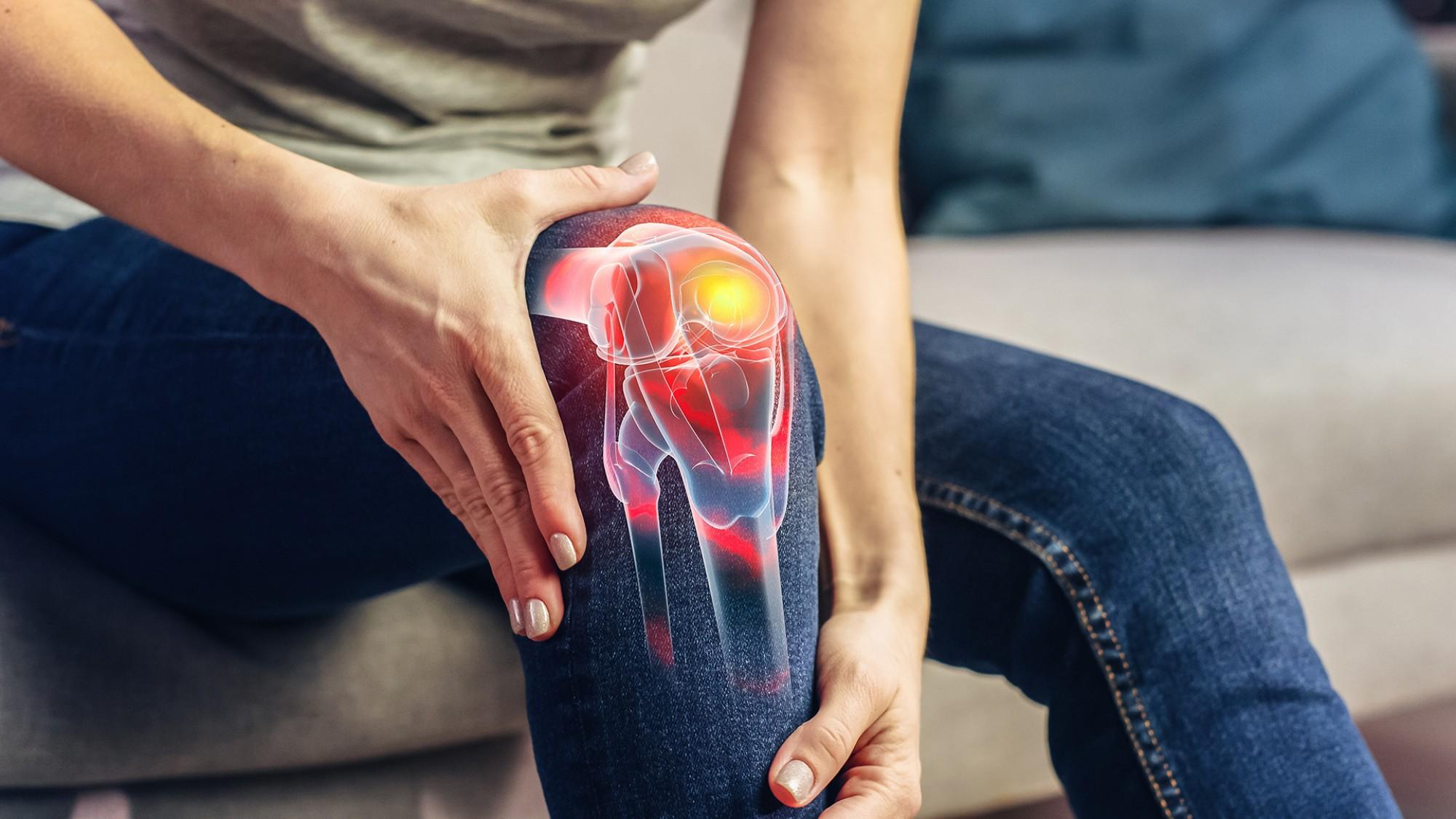
The immune system is designed to protect the body from harm. But sometimes, it turns against its own tissues, attacking joints, organs, and blood vessels. These conditions are known as autoimmune disorders, and they are among the most complex challenges in internal medicine. In Dubai, where healthcare access is excellent but awareness remains uneven, many patients endure years of unexplained pain, fatigue, and illness before receiving a diagnosis. Understanding these conditions is the first step toward relief.
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies the body’s own cells as threats. Instead of defending against viruses or bacteria, it launches attacks that cause chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common examples, where joints become swollen, painful, and eventually deformed if untreated. Systemic lupus erythematosus, or lupus, can affect the skin, kidneys, heart, and nervous system, producing a wide range of unpredictable symptoms. Other conditions include ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and vasculitis.
These diseases often present in ways that confuse both patients and doctors. Fatigue, fever, joint stiffness, skin rashes, and unexplained pain may come and go, making early recognition difficult. Many patients go through years of uncertainty before blood tests and imaging reveal the underlying cause. This delay can be devastating, as untreated autoimmune conditions may lead to permanent organ damage.
Modern diagnostics have improved outcomes dramatically. Blood markers such as ANA, RF, and anti-CCP antibodies, combined with X-rays and MRIs, allow for an accurate diagnosis. Once identified, treatment focuses on controlling inflammation and preventing damage. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids provide relief in the short term, while disease-modifying drugs and biologic therapies offer long-term control by targeting the immune system itself.
In Dubai, infusion centers and advanced clinics provide these biologic therapies under close supervision, making care more accessible than ever. Yet medical treatment is only part of the journey. Autoimmune conditions often affect people in their most productive years, interfering with work, family, and social life. Emotional support and lifestyle adaptation are crucial to living well.
Exercise, stress management, and balanced nutrition can ease symptoms and improve resilience. Patients benefit from physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and counseling. At IMH, specialists work alongside rheumatologists to create personalized care plans that address both physical and emotional needs.
Cultural sensitivity is also important. In the UAE’s diverse community, patients may have different expectations about treatment, ranging from traditional remedies to modern biologics. Doctors bridge this gap with open dialogue, respecting beliefs while ensuring evidence-based care.
Autoimmune disorders are lifelong, but they are not a life sentence. With timely diagnosis, advanced therapies, and comprehensive support, patients can manage symptoms and prevent complications. The key lies in awareness—recognizing that chronic pain, fatigue, or unexplained illness should not be ignored.
For those silently struggling, the message is clear: there are answers, and there is help. In Dubai’s healthcare environment, where innovation meets compassion, autoimmune disorders no longer have to mean uncertainty—they can be managed with strength, knowledge, and hope.





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









