Skin Biopsy
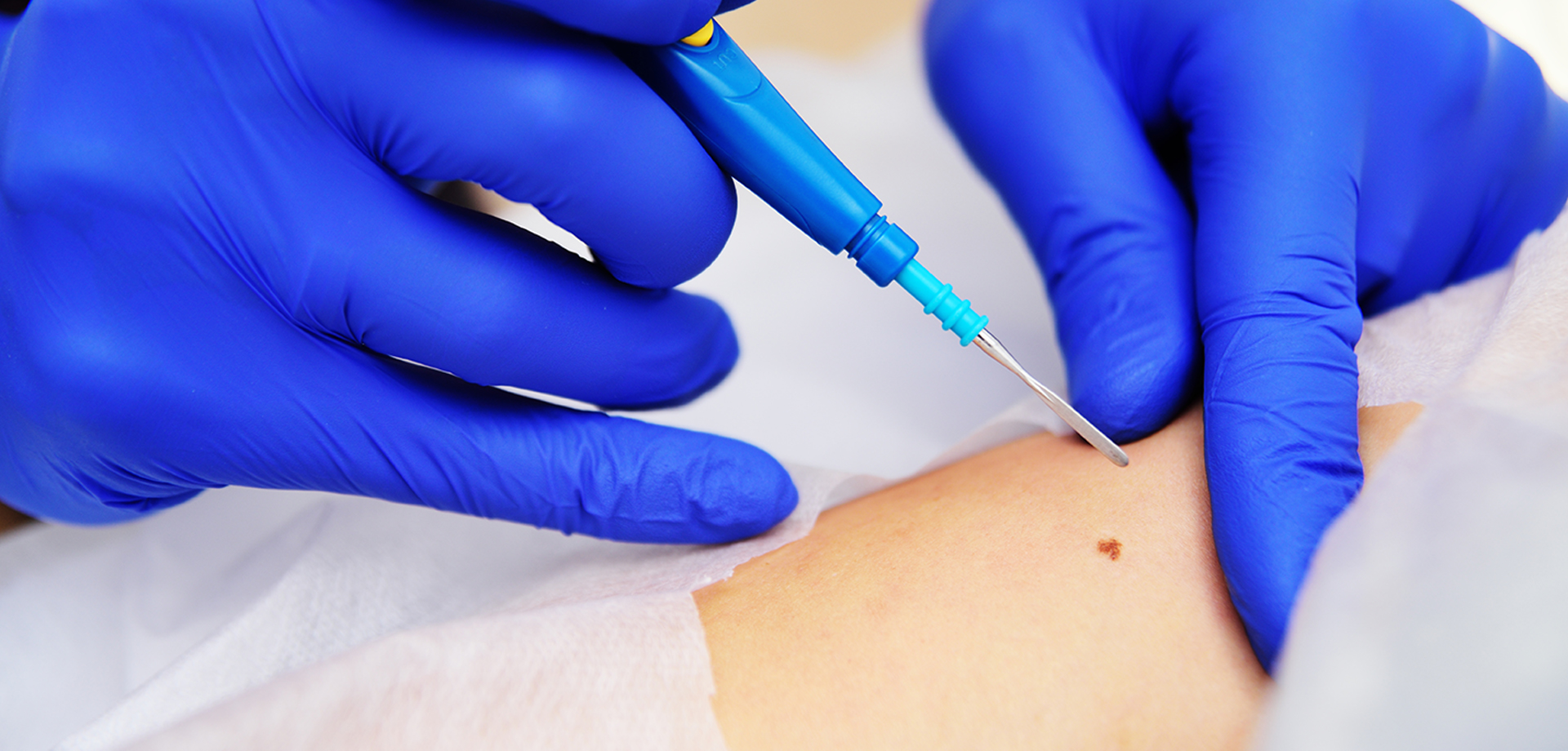
A skin biopsy is a diagnostic dermatological procedure performed to obtain a small sample of skin tissue for microscopic examination. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing a wide range of skin conditions, including inflammatory disorders, infections, autoimmune diseases, and skin cancers. When visual examination alone is insufficient to establish a diagnosis, biopsy provides definitive histopathological information that guides treatment decisions.
Skin biopsies are commonly recommended for persistent rashes, non-healing lesions, changing moles, unexplained pigmentation, or growths with atypical features. The procedure allows differentiation between benign and malignant conditions and helps determine disease severity and prognosis. Accurate diagnosis through biopsy prevents unnecessary treatment and ensures timely management of serious conditions.
The biopsy procedure is performed under local anesthesia to ensure comfort. Depending on the lesion’s size, depth, and location, different biopsy techniques may be used, including punch, shave, or excisional biopsy. The selected area is numbed, a tissue sample is obtained using sterile instruments, and the site is dressed appropriately. Sutures may be placed if required.
Following the procedure, the sample is sent to a pathology laboratory for detailed examination by a dermatopathologist. Results typically provide information on cellular structure, inflammation patterns, or malignant changes. This information enables dermatologists to tailor treatment precisely to the diagnosed condition.
Post-biopsy care involves keeping the area clean, monitoring for signs of infection, and attending follow-up appointments to discuss results. Healing usually occurs within one to two weeks. Skin biopsy is a safe and essential diagnostic tool in dermatology, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective, evidence-based care.
Skin biopsies are commonly recommended for persistent rashes, non-healing lesions, changing moles, unexplained pigmentation, or growths with atypical features. The procedure allows differentiation between benign and malignant conditions and helps determine disease severity and prognosis. Accurate diagnosis through biopsy prevents unnecessary treatment and ensures timely management of serious conditions.
The biopsy procedure is performed under local anesthesia to ensure comfort. Depending on the lesion’s size, depth, and location, different biopsy techniques may be used, including punch, shave, or excisional biopsy. The selected area is numbed, a tissue sample is obtained using sterile instruments, and the site is dressed appropriately. Sutures may be placed if required.
Following the procedure, the sample is sent to a pathology laboratory for detailed examination by a dermatopathologist. Results typically provide information on cellular structure, inflammation patterns, or malignant changes. This information enables dermatologists to tailor treatment precisely to the diagnosed condition.
Post-biopsy care involves keeping the area clean, monitoring for signs of infection, and attending follow-up appointments to discuss results. Healing usually occurs within one to two weeks. Skin biopsy is a safe and essential diagnostic tool in dermatology, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective, evidence-based care.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









