Septoplasty
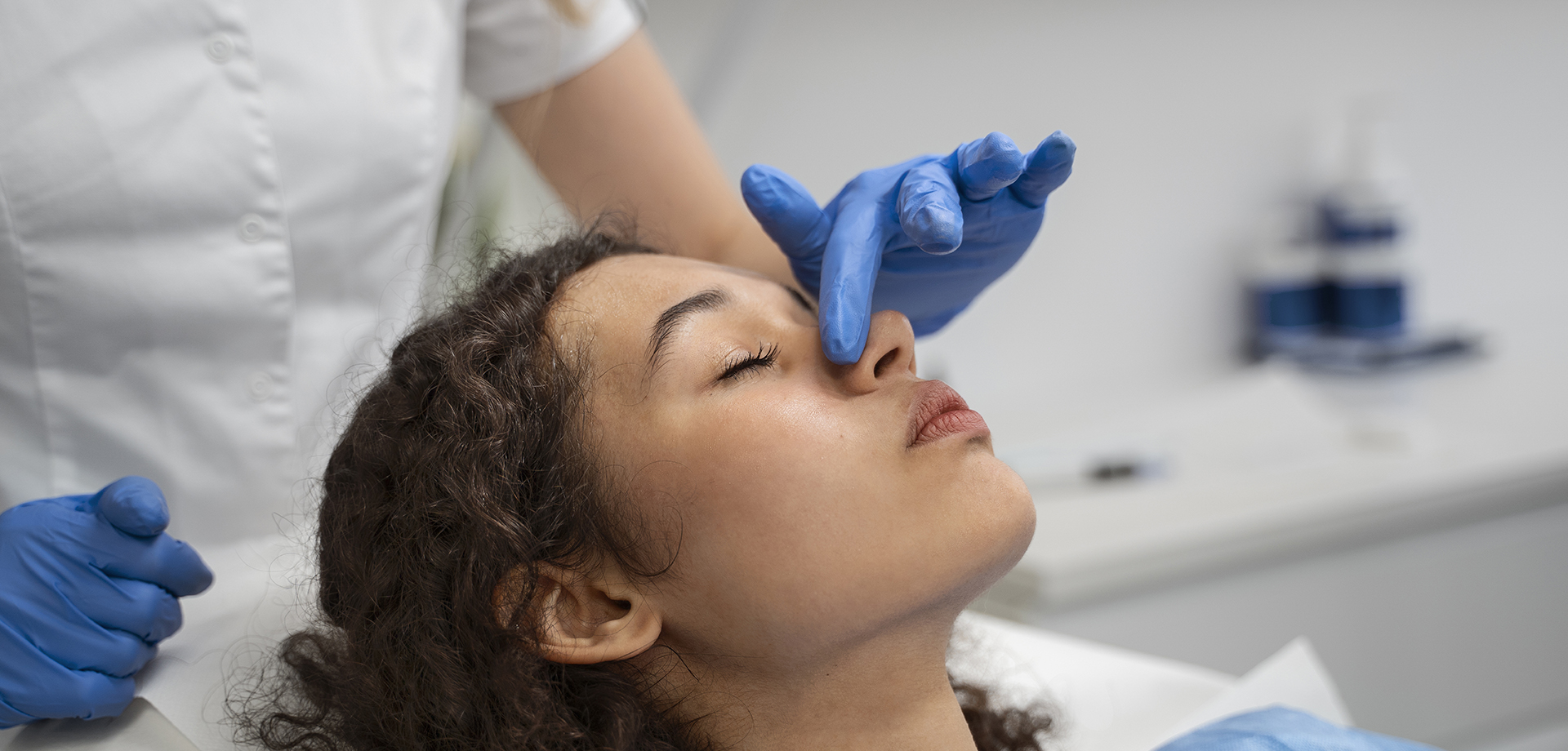
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure performed to correct a deviated nasal septum, a condition in which the cartilage and bone dividing the nasal cavity are displaced from the midline. A significantly deviated septum can obstruct airflow, impair nasal breathing, and contribute to sinus infections, nosebleeds, snoring, and sleep-related breathing disorders.
Septal deviation may be present from birth or develop due to trauma, including sports injuries or accidents. While many individuals with mild deviation remain asymptomatic, others experience persistent nasal blockage on one or both sides, mouth breathing, facial pressure, headaches, and recurrent sinusitis. Medical therapy may provide temporary relief by reducing mucosal swelling, but it cannot correct the underlying structural problem.
Septoplasty is indicated when nasal obstruction significantly affects quality of life or contributes to recurrent infections or sleep disturbance. The procedure is performed through the nostrils, avoiding external scars. Under general or local anesthesia, the surgeon elevates the nasal lining and reshapes, repositions, or removes the deviated portions of cartilage and bone to straighten the septum while preserving structural support.
Septoplasty may be performed as a standalone procedure or combined with turbinate reduction or sinus surgery. Surgical duration is usually short, and nasal packing or splints may be placed temporarily to support healing.
Postoperative symptoms include nasal congestion, mild discomfort, and temporary swelling. Breathing improvement becomes noticeable as swelling subsides over several weeks. Complications are uncommon when performed by experienced ENT surgeons.
Septoplasty provides long-term improvement in nasal airflow, reduces sinus symptoms, and enhances sleep quality, making it a highly effective solution for symptomatic septal deviation.
Septal deviation may be present from birth or develop due to trauma, including sports injuries or accidents. While many individuals with mild deviation remain asymptomatic, others experience persistent nasal blockage on one or both sides, mouth breathing, facial pressure, headaches, and recurrent sinusitis. Medical therapy may provide temporary relief by reducing mucosal swelling, but it cannot correct the underlying structural problem.
Septoplasty is indicated when nasal obstruction significantly affects quality of life or contributes to recurrent infections or sleep disturbance. The procedure is performed through the nostrils, avoiding external scars. Under general or local anesthesia, the surgeon elevates the nasal lining and reshapes, repositions, or removes the deviated portions of cartilage and bone to straighten the septum while preserving structural support.
Septoplasty may be performed as a standalone procedure or combined with turbinate reduction or sinus surgery. Surgical duration is usually short, and nasal packing or splints may be placed temporarily to support healing.
Postoperative symptoms include nasal congestion, mild discomfort, and temporary swelling. Breathing improvement becomes noticeable as swelling subsides over several weeks. Complications are uncommon when performed by experienced ENT surgeons.
Septoplasty provides long-term improvement in nasal airflow, reduces sinus symptoms, and enhances sleep quality, making it a highly effective solution for symptomatic septal deviation.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









