Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA)
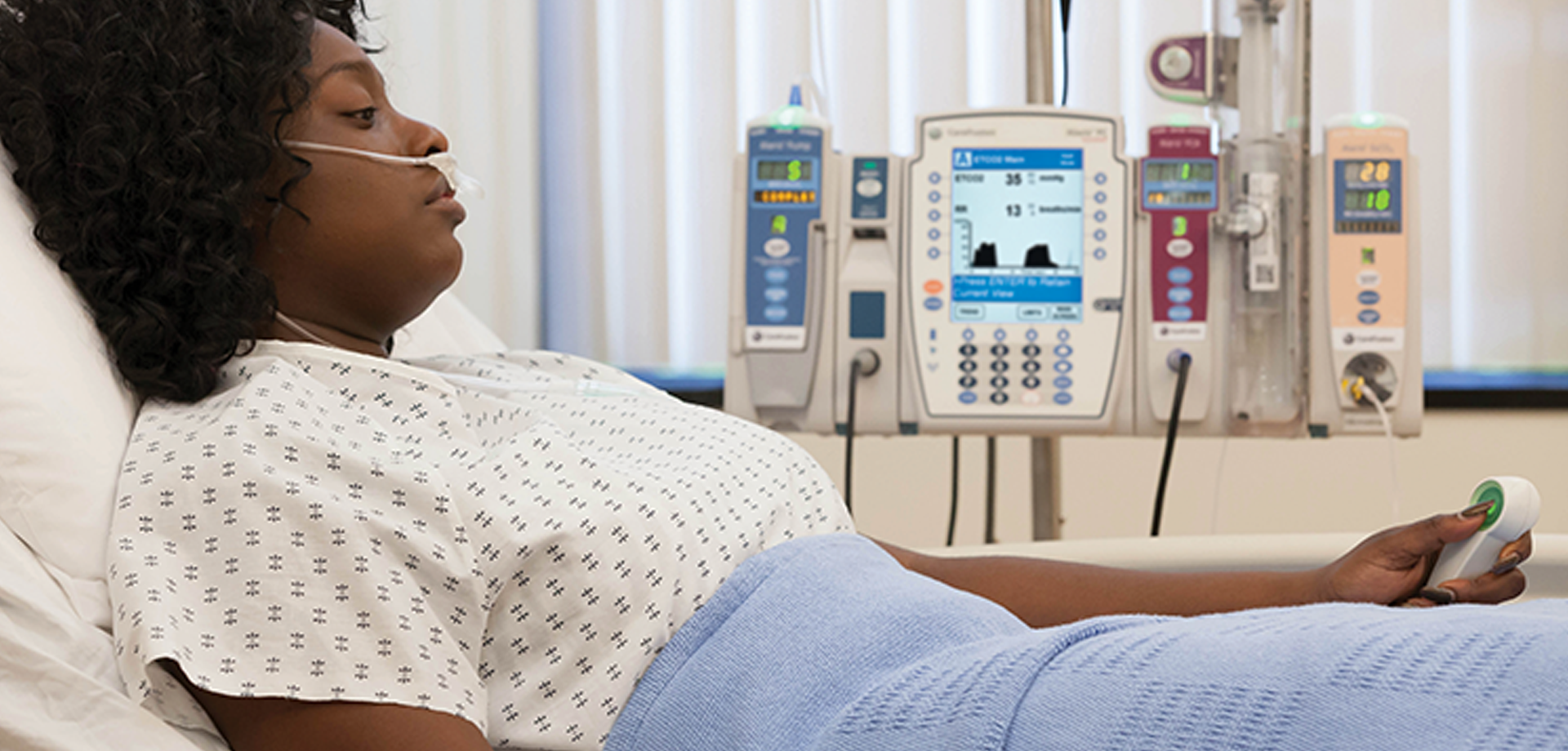
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is an advanced pain management technique that allows patients to self-administer predetermined doses of analgesic medication through a programmable infusion device. PCA is widely used in postoperative care and acute pain management to provide effective, individualized pain relief while maintaining safety through controlled dosing parameters. By empowering patients to manage their pain within medically defined limits, PCA improves comfort, satisfaction, and overall recovery.
The fundamental principle of PCA is that pain perception is subjective and varies significantly between individuals. Traditional nurse-administered pain medication schedules may result in delayed relief or fluctuating pain control. PCA addresses this by allowing patients to administer analgesia at the moment pain occurs, leading to more consistent pain control and reduced anxiety related to pain anticipation.
PCA systems are typically programmed to deliver intravenous opioids, though other agents may also be used depending on clinical needs. The device is configured with safety features including a fixed bolus dose, lockout interval, and maximum dose limits to prevent overdose. Only the patient is permitted to activate the device, ensuring that dosing reflects actual pain perception and reducing the risk of oversedation.
Before initiating PCA, a thorough patient assessment is conducted to ensure suitability. Patients must be cognitively intact, physically able to operate the device, and understand instructions regarding its use. Education plays a critical role in PCA success, as proper usage improves analgesic effectiveness and minimizes complications.
PCA is commonly used following major abdominal surgery, orthopedic procedures, thoracic surgery, and other operations associated with moderate to severe postoperative pain. It may also be employed in certain medical conditions requiring sustained pain control. By maintaining stable analgesic levels, PCA reduces pain spikes and promotes earlier mobilization, improved respiratory function, and faster recovery.
Continuous monitoring is essential during PCA therapy. Vital signs, pain scores, sedation level, and respiratory status are closely observed to detect adverse effects such as respiratory depression, nausea, or excessive sedation. PCA protocols are integrated into broader pain management strategies, often as part of multimodal analgesia.
The benefits of PCA include improved pain control, greater patient autonomy, reduced nursing workload for pain administration, and higher patient satisfaction. When properly managed, PCA provides safe, effective analgesia tailored to individual needs.
Patient-controlled analgesia remains a cornerstone of modern postoperative pain management, combining technological precision with patient-centered care to enhance recovery and comfort.
The fundamental principle of PCA is that pain perception is subjective and varies significantly between individuals. Traditional nurse-administered pain medication schedules may result in delayed relief or fluctuating pain control. PCA addresses this by allowing patients to administer analgesia at the moment pain occurs, leading to more consistent pain control and reduced anxiety related to pain anticipation.
PCA systems are typically programmed to deliver intravenous opioids, though other agents may also be used depending on clinical needs. The device is configured with safety features including a fixed bolus dose, lockout interval, and maximum dose limits to prevent overdose. Only the patient is permitted to activate the device, ensuring that dosing reflects actual pain perception and reducing the risk of oversedation.
Before initiating PCA, a thorough patient assessment is conducted to ensure suitability. Patients must be cognitively intact, physically able to operate the device, and understand instructions regarding its use. Education plays a critical role in PCA success, as proper usage improves analgesic effectiveness and minimizes complications.
PCA is commonly used following major abdominal surgery, orthopedic procedures, thoracic surgery, and other operations associated with moderate to severe postoperative pain. It may also be employed in certain medical conditions requiring sustained pain control. By maintaining stable analgesic levels, PCA reduces pain spikes and promotes earlier mobilization, improved respiratory function, and faster recovery.
Continuous monitoring is essential during PCA therapy. Vital signs, pain scores, sedation level, and respiratory status are closely observed to detect adverse effects such as respiratory depression, nausea, or excessive sedation. PCA protocols are integrated into broader pain management strategies, often as part of multimodal analgesia.
The benefits of PCA include improved pain control, greater patient autonomy, reduced nursing workload for pain administration, and higher patient satisfaction. When properly managed, PCA provides safe, effective analgesia tailored to individual needs.
Patient-controlled analgesia remains a cornerstone of modern postoperative pain management, combining technological precision with patient-centered care to enhance recovery and comfort.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









