Hysterectomy
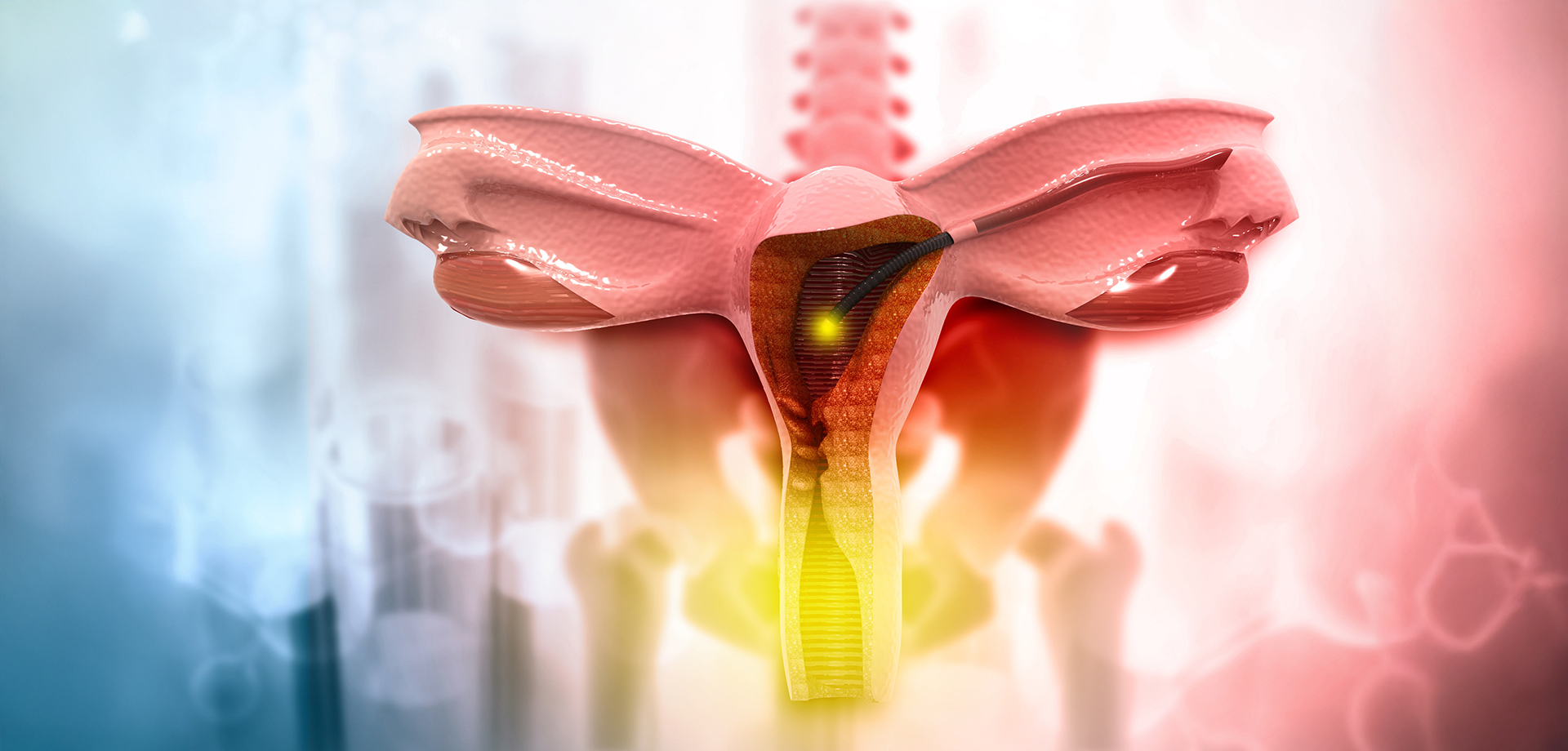
Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove the uterus and is one of the most common gynecological surgeries worldwide. It is indicated for a variety of benign and malignant conditions affecting the uterus that significantly impact a woman’s health, quality of life, or reproductive system. Depending on the underlying condition and patient factors, hysterectomy may be performed as a definitive and life-improving treatment.
Conditions that commonly require hysterectomy include uterine fibroids, abnormal uterine bleeding, adenomyosis, endometriosis, uterine prolapse, chronic pelvic pain, and cancers of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries. Symptoms leading to hysterectomy may include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure or pain, anemia, urinary symptoms, or failure of medical and less invasive treatments. In cancer cases, hysterectomy plays a critical role in curative treatment and disease control.
Hysterectomy can be classified based on the extent of surgery. A total hysterectomy involves removal of the uterus and cervix, while a subtotal hysterectomy removes only the uterus. In certain cases, the ovaries and fallopian tubes may also be removed, depending on age, disease risk, and cancer considerations. The surgical approach is individualized to ensure optimal outcomes.
Advances in surgical techniques have allowed hysterectomy to be performed using minimally invasive methods in many patients. Laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hysterectomy involve small incisions, reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery compared to open surgery. Vaginal hysterectomy may also be an option in selected cases. Open abdominal hysterectomy is reserved for large uteri, complex pathology, or advanced malignancy.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia following thorough preoperative evaluation, which includes imaging, blood tests, and gynecological assessment. Surgical planning considers symptom severity, reproductive goals, hormonal implications, and overall health. Multidisciplinary input may be required in oncology-related cases.
Postoperative recovery varies depending on the surgical approach. Most patients undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomy resume normal activities within a few weeks. Pain is typically well controlled, and patients receive guidance on activity restrictions, wound care, and hormonal considerations if ovaries are removed.
Hysterectomy provides definitive relief from debilitating uterine conditions and significantly improves quality of life. When performed for appropriate indications with modern techniques, it is a safe and effective procedure with excellent long-term outcomes.
Conditions that commonly require hysterectomy include uterine fibroids, abnormal uterine bleeding, adenomyosis, endometriosis, uterine prolapse, chronic pelvic pain, and cancers of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries. Symptoms leading to hysterectomy may include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure or pain, anemia, urinary symptoms, or failure of medical and less invasive treatments. In cancer cases, hysterectomy plays a critical role in curative treatment and disease control.
Hysterectomy can be classified based on the extent of surgery. A total hysterectomy involves removal of the uterus and cervix, while a subtotal hysterectomy removes only the uterus. In certain cases, the ovaries and fallopian tubes may also be removed, depending on age, disease risk, and cancer considerations. The surgical approach is individualized to ensure optimal outcomes.
Advances in surgical techniques have allowed hysterectomy to be performed using minimally invasive methods in many patients. Laparoscopic and robotic-assisted hysterectomy involve small incisions, reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery compared to open surgery. Vaginal hysterectomy may also be an option in selected cases. Open abdominal hysterectomy is reserved for large uteri, complex pathology, or advanced malignancy.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia following thorough preoperative evaluation, which includes imaging, blood tests, and gynecological assessment. Surgical planning considers symptom severity, reproductive goals, hormonal implications, and overall health. Multidisciplinary input may be required in oncology-related cases.
Postoperative recovery varies depending on the surgical approach. Most patients undergoing minimally invasive hysterectomy resume normal activities within a few weeks. Pain is typically well controlled, and patients receive guidance on activity restrictions, wound care, and hormonal considerations if ovaries are removed.
Hysterectomy provides definitive relief from debilitating uterine conditions and significantly improves quality of life. When performed for appropriate indications with modern techniques, it is a safe and effective procedure with excellent long-term outcomes.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









