Endocrine System Surgery
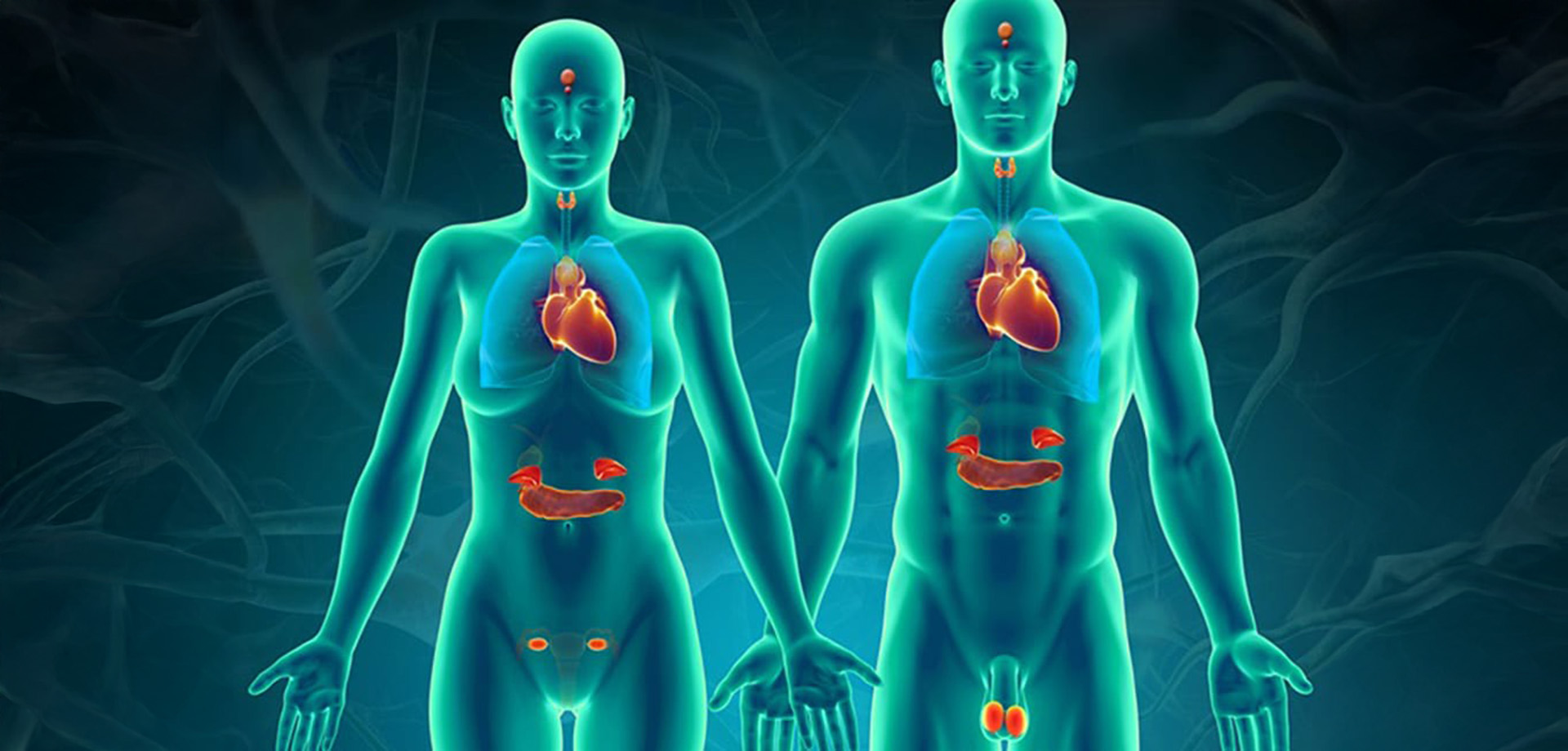
Endocrine system surgery focuses on the surgical treatment of disorders affecting hormone-producing glands, which play a critical role in regulating metabolism, growth, reproduction, blood sugar levels, calcium balance, and stress responses. The endocrine system includes glands such as the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas (endocrine component), and certain neuroendocrine tissues. Surgical intervention is often required when endocrine disorders cause significant symptoms, hormonal imbalance, or malignancy.
Endocrine diseases may present subtly, with symptoms such as weight changes, fatigue, palpitations, heat or cold intolerance, bone loss, hypertension, or unexplained metabolic abnormalities. Because hormonal disorders affect multiple organ systems, accurate diagnosis and targeted surgical management are essential. Endocrine surgery aims to remove diseased tissue while preserving normal gland function whenever possible.
Common conditions requiring endocrine surgery include thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism, parathyroid adenomas causing high calcium levels, adrenal tumors producing excess hormones, and neuroendocrine tumors. Surgical intervention is also indicated when imaging or biopsy suggests malignancy, functional hormone overproduction, or compression of surrounding structures.
Preoperative evaluation is meticulous and includes hormonal blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT, MRI, or nuclear scans, and fine-needle aspiration biopsies where appropriate. Multidisciplinary coordination with endocrinologists, radiologists, pathologists, and anesthesiologists ensures accurate diagnosis and optimal surgical planning.
Endocrine system surgery is typically performed using minimally invasive techniques when feasible. Advances in surgical technology allow precise gland removal through small incisions, reducing scarring, pain, and recovery time. In thyroid and parathyroid surgery, nerve monitoring is often used to protect vocal cord function. Adrenal surgery is commonly performed laparoscopically to minimize surgical trauma.
Procedures are carried out under general anesthesia in specialized operating theaters. Surgeons take great care to preserve surrounding nerves, blood vessels, and normal gland tissue. In cancer cases, appropriate lymph node removal may be performed to ensure complete disease clearance.
Postoperative care focuses on monitoring hormone levels, calcium balance, blood pressure, and overall recovery. Some patients may require temporary or long-term hormone replacement therapy depending on the extent of surgery. Most patients experience significant symptom improvement and rapid recovery following endocrine surgery.
Endocrine system surgery provides definitive treatment for a wide range of hormone-related disorders. When performed by experienced surgeons with appropriate multidisciplinary support, it delivers excellent outcomes, restores hormonal balance, and significantly improves quality of life.
Endocrine diseases may present subtly, with symptoms such as weight changes, fatigue, palpitations, heat or cold intolerance, bone loss, hypertension, or unexplained metabolic abnormalities. Because hormonal disorders affect multiple organ systems, accurate diagnosis and targeted surgical management are essential. Endocrine surgery aims to remove diseased tissue while preserving normal gland function whenever possible.
Common conditions requiring endocrine surgery include thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism, parathyroid adenomas causing high calcium levels, adrenal tumors producing excess hormones, and neuroendocrine tumors. Surgical intervention is also indicated when imaging or biopsy suggests malignancy, functional hormone overproduction, or compression of surrounding structures.
Preoperative evaluation is meticulous and includes hormonal blood tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT, MRI, or nuclear scans, and fine-needle aspiration biopsies where appropriate. Multidisciplinary coordination with endocrinologists, radiologists, pathologists, and anesthesiologists ensures accurate diagnosis and optimal surgical planning.
Endocrine system surgery is typically performed using minimally invasive techniques when feasible. Advances in surgical technology allow precise gland removal through small incisions, reducing scarring, pain, and recovery time. In thyroid and parathyroid surgery, nerve monitoring is often used to protect vocal cord function. Adrenal surgery is commonly performed laparoscopically to minimize surgical trauma.
Procedures are carried out under general anesthesia in specialized operating theaters. Surgeons take great care to preserve surrounding nerves, blood vessels, and normal gland tissue. In cancer cases, appropriate lymph node removal may be performed to ensure complete disease clearance.
Postoperative care focuses on monitoring hormone levels, calcium balance, blood pressure, and overall recovery. Some patients may require temporary or long-term hormone replacement therapy depending on the extent of surgery. Most patients experience significant symptom improvement and rapid recovery following endocrine surgery.
Endocrine system surgery provides definitive treatment for a wide range of hormone-related disorders. When performed by experienced surgeons with appropriate multidisciplinary support, it delivers excellent outcomes, restores hormonal balance, and significantly improves quality of life.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









