Appendectomy
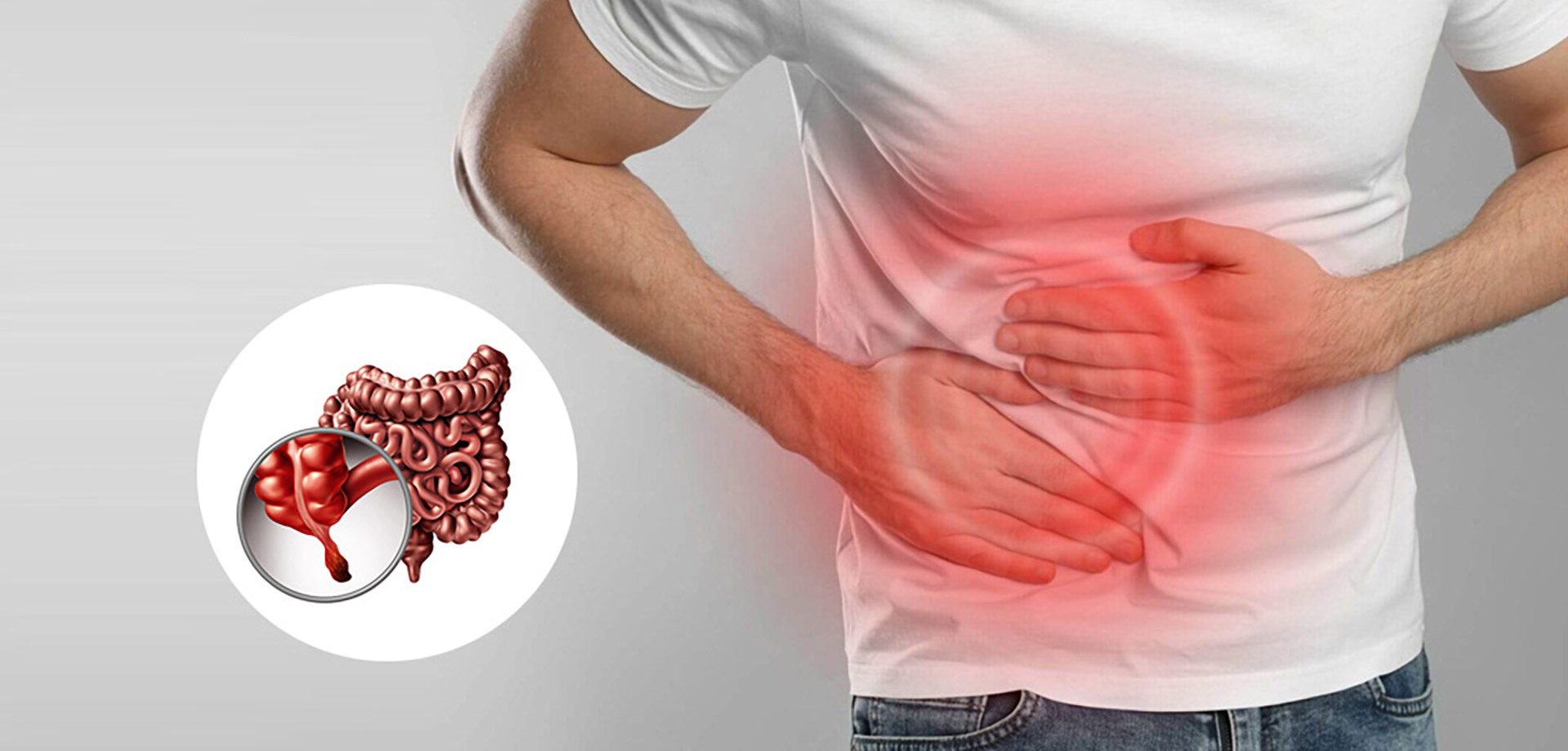
Appendectomy is a common and well-established surgical procedure performed to remove the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine. Appendicitis, or inflammation of the appendix, is a medical emergency that can occur at any age and requires prompt surgical intervention to prevent serious complications such as rupture, abscess formation, or widespread infection.
Appendicitis typically presents with abdominal pain that begins near the navel and shifts to the lower right abdomen, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite. The condition develops when the appendix becomes blocked, leading to bacterial infection and inflammation. Without timely treatment, the inflamed appendix can rupture, significantly increasing morbidity and recovery time.
Appendectomy is indicated in patients with suspected or confirmed appendicitis. Diagnosis is based on clinical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan. Early surgical intervention is critical to prevent complications and ensure optimal outcomes.
The procedure can be performed using either a laparoscopic or open approach. Laparoscopic appendectomy is the preferred method in most cases, as it involves small incisions, reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and lower risk of wound infection. An open appendectomy may be necessary in cases of ruptured appendix, extensive infection, or when minimally invasive surgery is not suitable.
Appendectomy is performed under general anesthesia. During laparoscopic surgery, a camera and specialized instruments are used to visualize and remove the inflamed appendix safely. The surgical area is thoroughly cleaned to reduce infection risk, particularly in cases of perforation.
Following surgery, patients are monitored for pain control, infection, and return of normal bowel function. Most individuals undergoing uncomplicated appendectomy can resume normal activities within one to two weeks, with shorter recovery times after laparoscopic surgery. Antibiotics may be prescribed depending on the severity of infection.
Appendectomy is a definitive treatment for appendicitis and carries a high success rate when performed promptly. Early intervention minimizes complications, shortens hospital stay, and allows rapid return to normal daily life. With modern surgical techniques and postoperative care, appendectomy remains a safe and highly effective emergency surgical procedure.
Appendicitis typically presents with abdominal pain that begins near the navel and shifts to the lower right abdomen, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite. The condition develops when the appendix becomes blocked, leading to bacterial infection and inflammation. Without timely treatment, the inflamed appendix can rupture, significantly increasing morbidity and recovery time.
Appendectomy is indicated in patients with suspected or confirmed appendicitis. Diagnosis is based on clinical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan. Early surgical intervention is critical to prevent complications and ensure optimal outcomes.
The procedure can be performed using either a laparoscopic or open approach. Laparoscopic appendectomy is the preferred method in most cases, as it involves small incisions, reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and lower risk of wound infection. An open appendectomy may be necessary in cases of ruptured appendix, extensive infection, or when minimally invasive surgery is not suitable.
Appendectomy is performed under general anesthesia. During laparoscopic surgery, a camera and specialized instruments are used to visualize and remove the inflamed appendix safely. The surgical area is thoroughly cleaned to reduce infection risk, particularly in cases of perforation.
Following surgery, patients are monitored for pain control, infection, and return of normal bowel function. Most individuals undergoing uncomplicated appendectomy can resume normal activities within one to two weeks, with shorter recovery times after laparoscopic surgery. Antibiotics may be prescribed depending on the severity of infection.
Appendectomy is a definitive treatment for appendicitis and carries a high success rate when performed promptly. Early intervention minimizes complications, shortens hospital stay, and allows rapid return to normal daily life. With modern surgical techniques and postoperative care, appendectomy remains a safe and highly effective emergency surgical procedure.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









