Abdominal Surgery
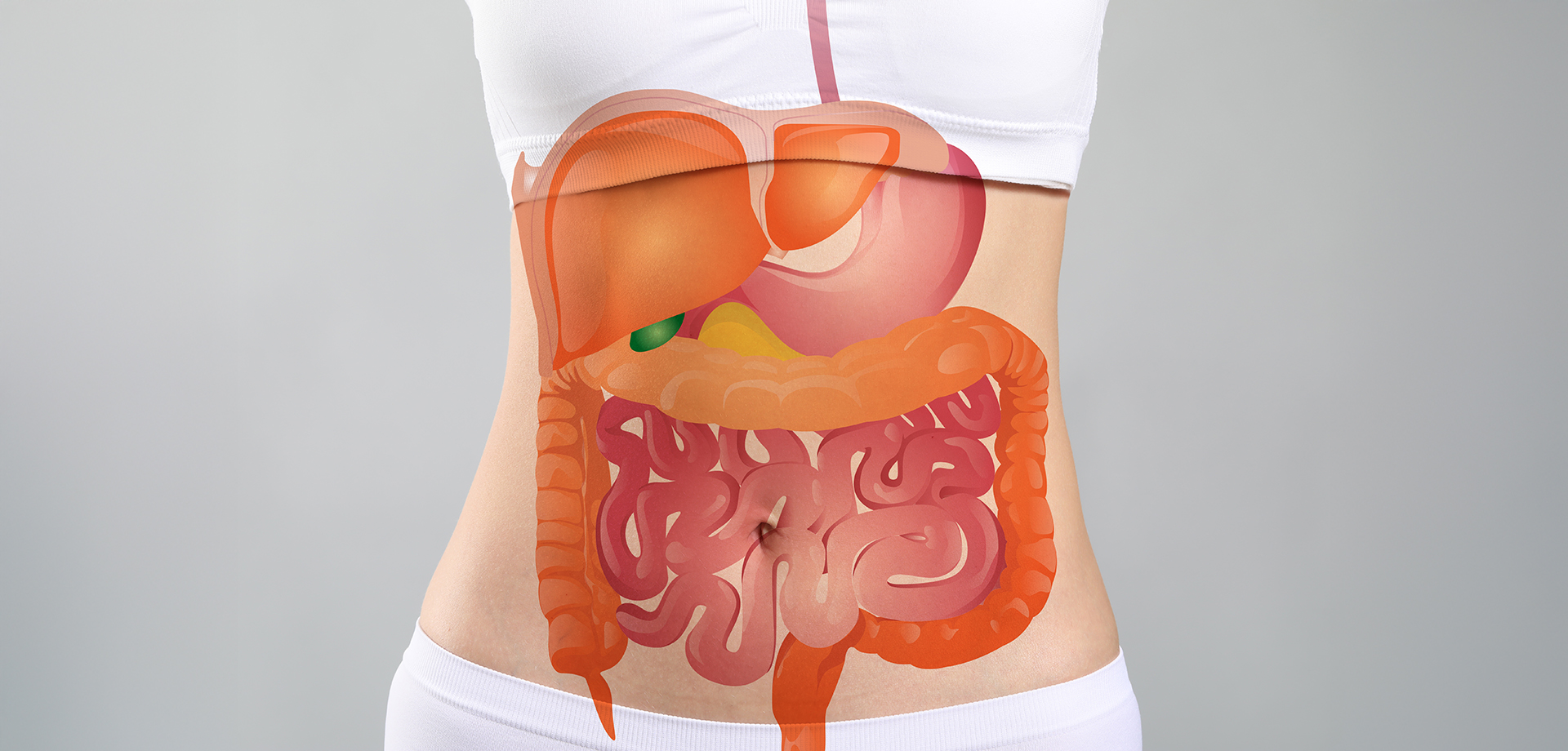
Abdominal surgery refers to a broad range of surgical procedures performed to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the organs within the abdominal cavity. These organs include the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, appendix, and abdominal blood vessels. Abdominal conditions can present with pain, obstruction, infection, bleeding, or organ dysfunction, and timely surgical intervention is often essential to prevent complications and restore normal function.
Abdominal surgery may be performed for both elective and emergency indications. Elective procedures address chronic or progressive conditions such as tumors, hernias, gallbladder disease, intestinal disorders, or inflammatory conditions. Emergency abdominal surgery is required in situations such as intestinal perforation, bowel obstruction, internal bleeding, ruptured appendix, or abdominal trauma. Accurate diagnosis and prompt surgical decision-making are critical in these scenarios.
The surgical approach depends on the underlying condition, patient health status, and urgency of intervention. Modern abdominal surgery increasingly favors minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, which involve small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments. Laparoscopic surgery offers advantages including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and lower risk of wound complications. In complex cases or emergencies, open abdominal surgery may be required to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Preoperative evaluation is comprehensive and includes clinical assessment, laboratory investigations, and imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. This ensures accurate diagnosis and helps surgeons plan the most appropriate approach. Multidisciplinary collaboration may be involved, particularly when abdominal surgery overlaps with oncology, gastroenterology, or vascular care.
Abdominal surgery is performed under general anesthesia in a fully equipped operating theater. During the procedure, surgeons carefully address the diseased organ while protecting surrounding structures. Advanced surgical techniques and intraoperative monitoring enhance precision and patient safety.
Postoperative care focuses on pain management, early mobilization, restoration of bowel function, and prevention of complications such as infection or blood clots. Recovery time varies depending on the procedure performed, but minimally invasive surgery allows many patients to resume normal activities within a shorter period.
Abdominal surgery remains a cornerstone of general surgery. When performed using modern techniques and individualized patient care, it provides effective treatment for a wide range of conditions, improves survival in emergency situations, and significantly enhances quality of life.
Abdominal surgery may be performed for both elective and emergency indications. Elective procedures address chronic or progressive conditions such as tumors, hernias, gallbladder disease, intestinal disorders, or inflammatory conditions. Emergency abdominal surgery is required in situations such as intestinal perforation, bowel obstruction, internal bleeding, ruptured appendix, or abdominal trauma. Accurate diagnosis and prompt surgical decision-making are critical in these scenarios.
The surgical approach depends on the underlying condition, patient health status, and urgency of intervention. Modern abdominal surgery increasingly favors minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, which involve small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments. Laparoscopic surgery offers advantages including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery, and lower risk of wound complications. In complex cases or emergencies, open abdominal surgery may be required to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Preoperative evaluation is comprehensive and includes clinical assessment, laboratory investigations, and imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. This ensures accurate diagnosis and helps surgeons plan the most appropriate approach. Multidisciplinary collaboration may be involved, particularly when abdominal surgery overlaps with oncology, gastroenterology, or vascular care.
Abdominal surgery is performed under general anesthesia in a fully equipped operating theater. During the procedure, surgeons carefully address the diseased organ while protecting surrounding structures. Advanced surgical techniques and intraoperative monitoring enhance precision and patient safety.
Postoperative care focuses on pain management, early mobilization, restoration of bowel function, and prevention of complications such as infection or blood clots. Recovery time varies depending on the procedure performed, but minimally invasive surgery allows many patients to resume normal activities within a shorter period.
Abdominal surgery remains a cornerstone of general surgery. When performed using modern techniques and individualized patient care, it provides effective treatment for a wide range of conditions, improves survival in emergency situations, and significantly enhances quality of life.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









