Liver Biopsy
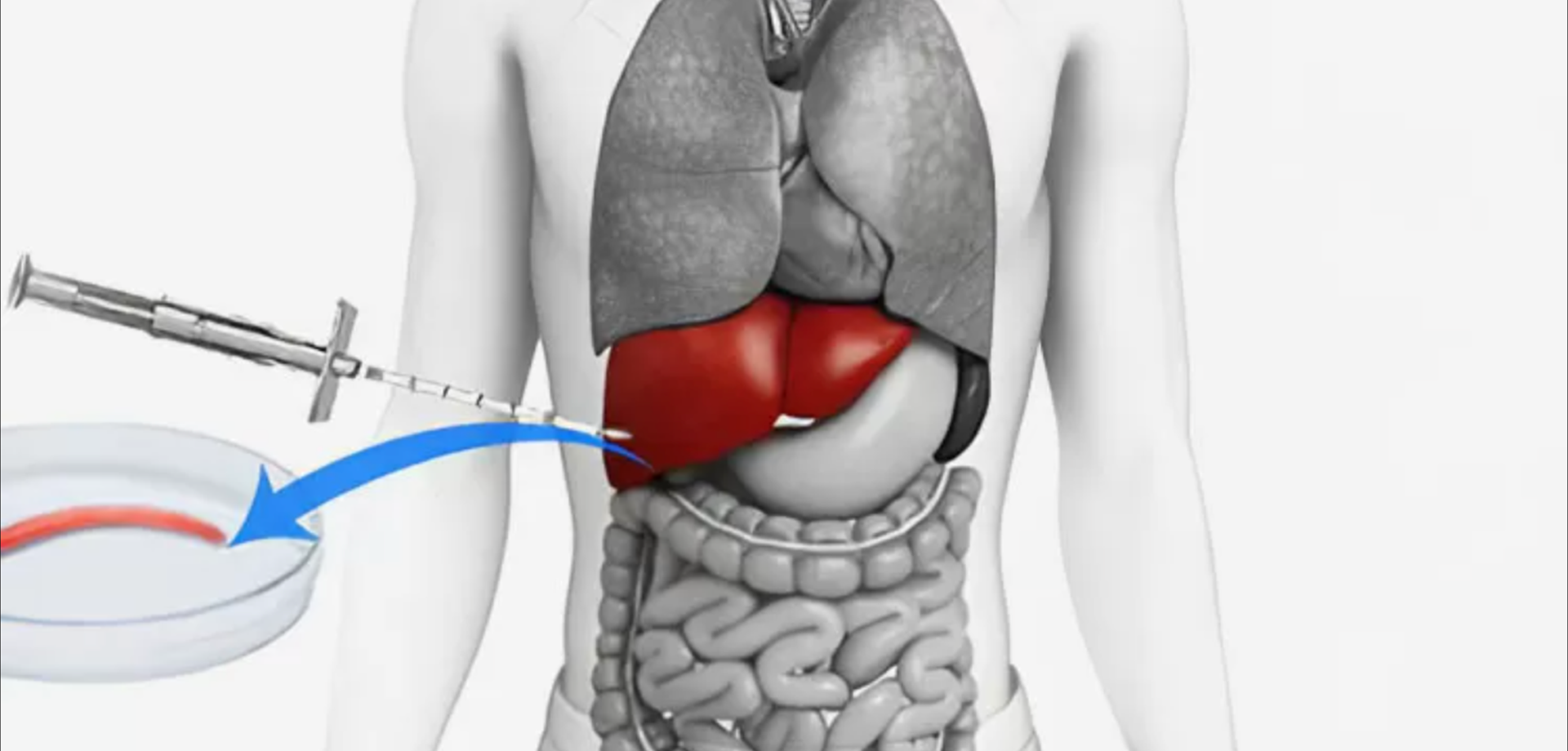
Liver biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to obtain a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination. Despite advances in non-invasive liver testing, liver biopsy remains the gold standard for assessing the severity, cause, and progression of many liver diseases. It provides critical information that cannot always be obtained through blood tests or imaging alone, particularly when treatment decisions depend on accurate staging of liver damage.
The procedure involves removing a small core of liver tissue using a specialized needle. Liver biopsy can be performed through different approaches depending on patient factors and clinical indications. The most common method is percutaneous biopsy, where the needle is inserted through the skin under imaging guidance. In selected cases, a transjugular approach may be used, particularly in patients with bleeding risk or ascites.
Liver biopsy is indicated in a wide range of conditions, including chronic viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, unexplained liver enzyme abnormalities, autoimmune liver diseases, metabolic liver disorders, and suspected liver cirrhosis. It is also used to assess liver involvement in systemic diseases and to evaluate unexplained liver masses.
Before the procedure, patients undergo careful evaluation including blood tests and imaging to minimize risks. Liver biopsy is typically performed under local anesthesia, sometimes with mild sedation, and is guided by ultrasound or other imaging modalities to ensure accuracy and safety. The procedure itself usually takes only a few minutes.
Following the biopsy, patients are monitored for several hours to ensure there are no complications such as bleeding or pain. Most patients experience mild discomfort at the biopsy site, which resolves quickly. Serious complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by experienced clinicians with appropriate precautions.
The liver tissue sample is examined by a pathologist to assess inflammation, fibrosis, fat content, and cellular abnormalities. These findings guide diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment decisions, including medication selection, lifestyle modification, or referral for advanced care. Liver biopsy also plays an important role in monitoring disease progression and response to therapy.
Liver biopsy remains a vital tool in hepatology and gastroenterology. When used appropriately, it provides definitive diagnostic insight, supports personalized treatment strategies, and improves long-term outcomes in patients with liver disease.
The procedure involves removing a small core of liver tissue using a specialized needle. Liver biopsy can be performed through different approaches depending on patient factors and clinical indications. The most common method is percutaneous biopsy, where the needle is inserted through the skin under imaging guidance. In selected cases, a transjugular approach may be used, particularly in patients with bleeding risk or ascites.
Liver biopsy is indicated in a wide range of conditions, including chronic viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, unexplained liver enzyme abnormalities, autoimmune liver diseases, metabolic liver disorders, and suspected liver cirrhosis. It is also used to assess liver involvement in systemic diseases and to evaluate unexplained liver masses.
Before the procedure, patients undergo careful evaluation including blood tests and imaging to minimize risks. Liver biopsy is typically performed under local anesthesia, sometimes with mild sedation, and is guided by ultrasound or other imaging modalities to ensure accuracy and safety. The procedure itself usually takes only a few minutes.
Following the biopsy, patients are monitored for several hours to ensure there are no complications such as bleeding or pain. Most patients experience mild discomfort at the biopsy site, which resolves quickly. Serious complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by experienced clinicians with appropriate precautions.
The liver tissue sample is examined by a pathologist to assess inflammation, fibrosis, fat content, and cellular abnormalities. These findings guide diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment decisions, including medication selection, lifestyle modification, or referral for advanced care. Liver biopsy also plays an important role in monitoring disease progression and response to therapy.
Liver biopsy remains a vital tool in hepatology and gastroenterology. When used appropriately, it provides definitive diagnostic insight, supports personalized treatment strategies, and improves long-term outcomes in patients with liver disease.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









