Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
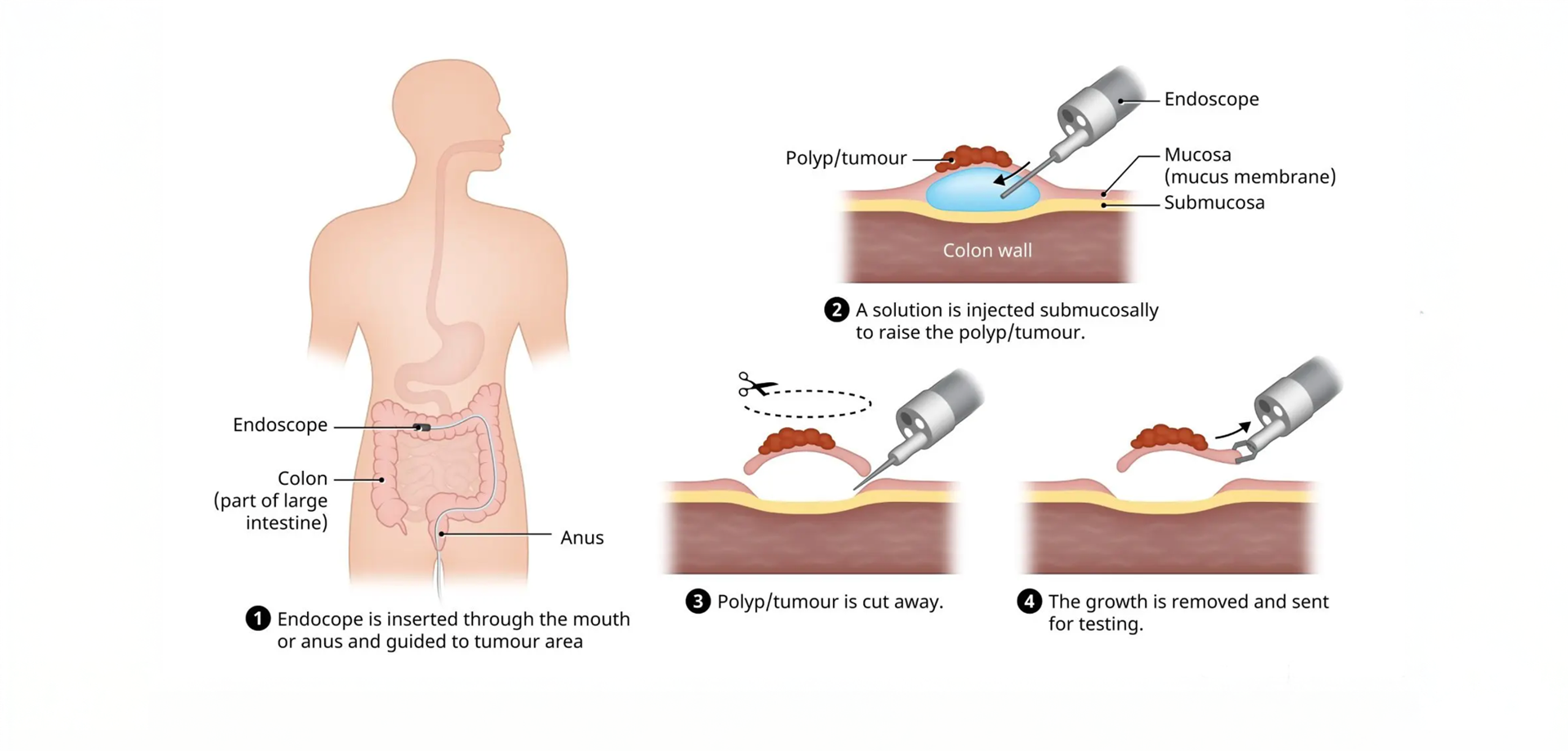
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) is an advanced therapeutic endoscopic procedure used to remove large, complex, or high-risk lesions from the gastrointestinal tract, including early-stage cancers. It represents a major advancement in minimally invasive gastroenterology, allowing curative treatment of selected gastrointestinal cancers without the need for open or laparoscopic surgery. ESD is particularly valuable in preserving organ function while achieving complete lesion removal.
Unlike conventional endoscopic techniques, ESD enables en bloc resection, meaning the lesion is removed in one single piece regardless of size. This is especially important for accurate pathological assessment, as it allows precise evaluation of margins, depth of invasion, and cancer staging. En bloc resection significantly reduces the risk of residual disease and local recurrence.
ESD is most commonly performed for early cancers and high-grade precancerous lesions of the stomach, esophagus, colon, and rectum that are confined to the superficial layers of the gastrointestinal wall. It is also used for large flat lesions and recurrent lesions that cannot be adequately treated with standard polypectomy or EMR. Careful patient selection is essential to ensure that lesions are suitable for curative endoscopic treatment.
The procedure is performed using a specialized endoscope equipped with precision cutting instruments. After marking the lesion borders, fluid is injected into the submucosal layer to lift the lesion away from the underlying muscle. This creates a safe plane for dissection and allows controlled removal of the lesion while minimizing the risk of perforation. The procedure requires advanced technical expertise and is typically performed by highly trained endoscopists.
ESD is carried out under sedation or general anesthesia in a specialized endoscopy unit with continuous monitoring. Although the procedure may take longer than conventional endoscopic resections, its precision and long-term benefits outweigh the extended procedural time. Patients are carefully monitored after the procedure for potential complications such as bleeding, which are promptly managed endoscopically if they occur.
Recovery following ESD is generally faster than surgical alternatives, with shorter hospital stays and preservation of normal gastrointestinal anatomy. Histopathological analysis of the resected specimen guides further management and determines whether additional treatment or surveillance is required.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection has transformed the management of early gastrointestinal cancers. When performed in appropriately selected patients, it offers curative outcomes, reduced morbidity, and excellent long-term disease control while avoiding the risks associated with major surgery.
Unlike conventional endoscopic techniques, ESD enables en bloc resection, meaning the lesion is removed in one single piece regardless of size. This is especially important for accurate pathological assessment, as it allows precise evaluation of margins, depth of invasion, and cancer staging. En bloc resection significantly reduces the risk of residual disease and local recurrence.
ESD is most commonly performed for early cancers and high-grade precancerous lesions of the stomach, esophagus, colon, and rectum that are confined to the superficial layers of the gastrointestinal wall. It is also used for large flat lesions and recurrent lesions that cannot be adequately treated with standard polypectomy or EMR. Careful patient selection is essential to ensure that lesions are suitable for curative endoscopic treatment.
The procedure is performed using a specialized endoscope equipped with precision cutting instruments. After marking the lesion borders, fluid is injected into the submucosal layer to lift the lesion away from the underlying muscle. This creates a safe plane for dissection and allows controlled removal of the lesion while minimizing the risk of perforation. The procedure requires advanced technical expertise and is typically performed by highly trained endoscopists.
ESD is carried out under sedation or general anesthesia in a specialized endoscopy unit with continuous monitoring. Although the procedure may take longer than conventional endoscopic resections, its precision and long-term benefits outweigh the extended procedural time. Patients are carefully monitored after the procedure for potential complications such as bleeding, which are promptly managed endoscopically if they occur.
Recovery following ESD is generally faster than surgical alternatives, with shorter hospital stays and preservation of normal gastrointestinal anatomy. Histopathological analysis of the resected specimen guides further management and determines whether additional treatment or surveillance is required.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection has transformed the management of early gastrointestinal cancers. When performed in appropriately selected patients, it offers curative outcomes, reduced morbidity, and excellent long-term disease control while avoiding the risks associated with major surgery.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









