Coronary Angioplasty
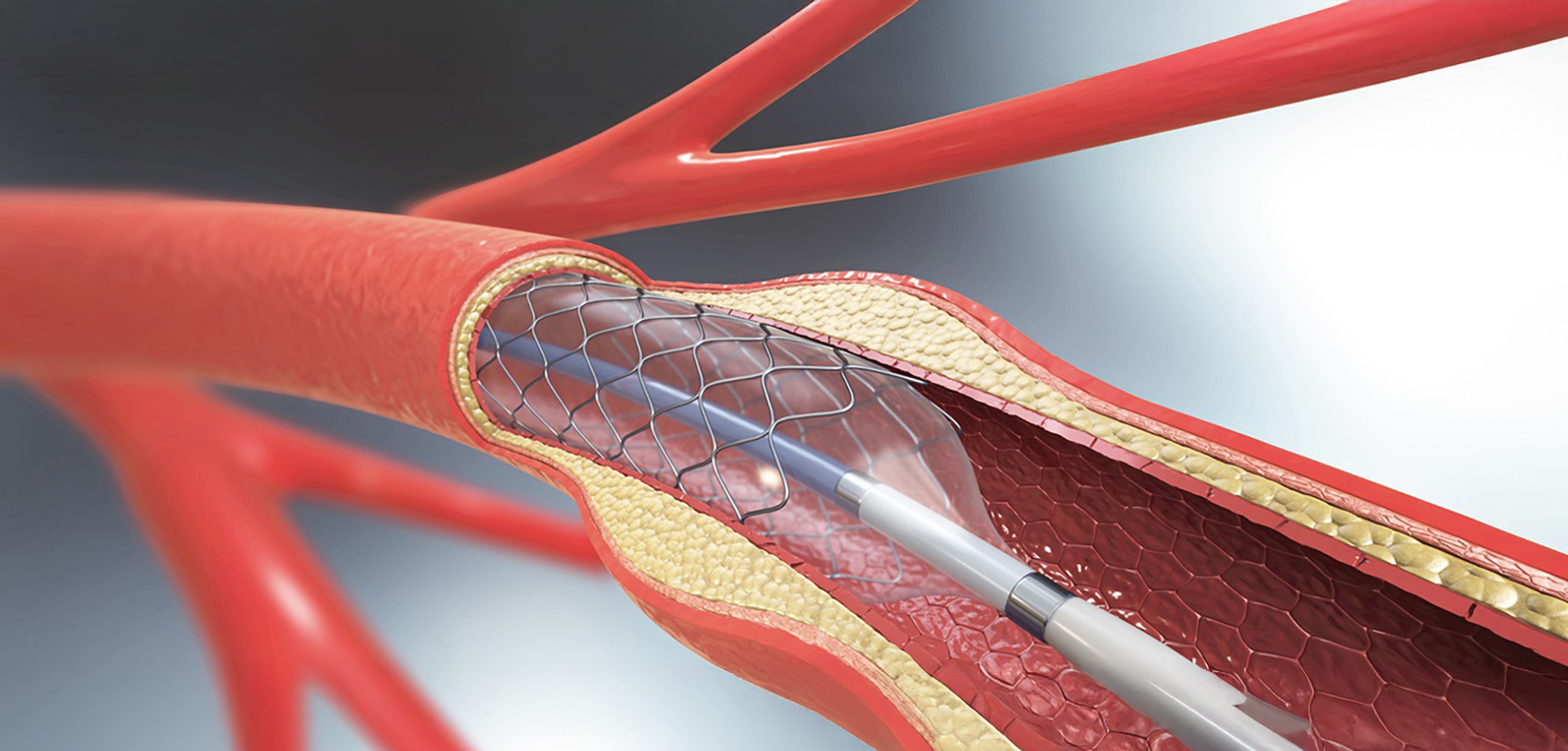
Coronary angioplasty is a minimally invasive interventional cardiology procedure performed to restore blood flow through narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. It is commonly used in patients with symptomatic coronary artery disease and in emergency settings such as acute heart attacks, where rapid reperfusion is critical to preserve heart muscle and improve survival.
The procedure involves advancing a catheter to the affected coronary artery and using specialized techniques to widen the narrowed segment. Angioplasty improves blood supply to the myocardium, relieving symptoms such as chest pain and breathlessness while reducing the risk of future cardiac events.
Coronary angioplasty is frequently performed following diagnostic coronary angiography when significant arterial narrowing is identified. It may be planned electively for stable coronary disease or performed urgently in acute coronary syndromes. The decision to proceed with angioplasty is based on anatomical findings, symptom severity, and overall patient risk profile.
Modern angioplasty techniques are supported by advanced imaging and physiologic assessment tools, allowing precise treatment of the diseased segment while minimizing impact on healthy vessels. The procedure is performed in a cardiac catheterization laboratory by experienced interventional cardiologists with continuous monitoring.
Following angioplasty, patients are observed for hemodynamic stability and access-site integrity. Cardiac recovery planning begins early, focusing on symptom resolution, functional improvement, and prevention of disease progression through structured follow-up.
Coronary angioplasty has transformed the management of coronary artery disease by providing an effective, less invasive alternative to surgery for many patients. When integrated into comprehensive cardiac care, it significantly improves outcomes and quality of life.
The procedure involves advancing a catheter to the affected coronary artery and using specialized techniques to widen the narrowed segment. Angioplasty improves blood supply to the myocardium, relieving symptoms such as chest pain and breathlessness while reducing the risk of future cardiac events.
Coronary angioplasty is frequently performed following diagnostic coronary angiography when significant arterial narrowing is identified. It may be planned electively for stable coronary disease or performed urgently in acute coronary syndromes. The decision to proceed with angioplasty is based on anatomical findings, symptom severity, and overall patient risk profile.
Modern angioplasty techniques are supported by advanced imaging and physiologic assessment tools, allowing precise treatment of the diseased segment while minimizing impact on healthy vessels. The procedure is performed in a cardiac catheterization laboratory by experienced interventional cardiologists with continuous monitoring.
Following angioplasty, patients are observed for hemodynamic stability and access-site integrity. Cardiac recovery planning begins early, focusing on symptom resolution, functional improvement, and prevention of disease progression through structured follow-up.
Coronary angioplasty has transformed the management of coronary artery disease by providing an effective, less invasive alternative to surgery for many patients. When integrated into comprehensive cardiac care, it significantly improves outcomes and quality of life.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









