Balloon Sinuplasty
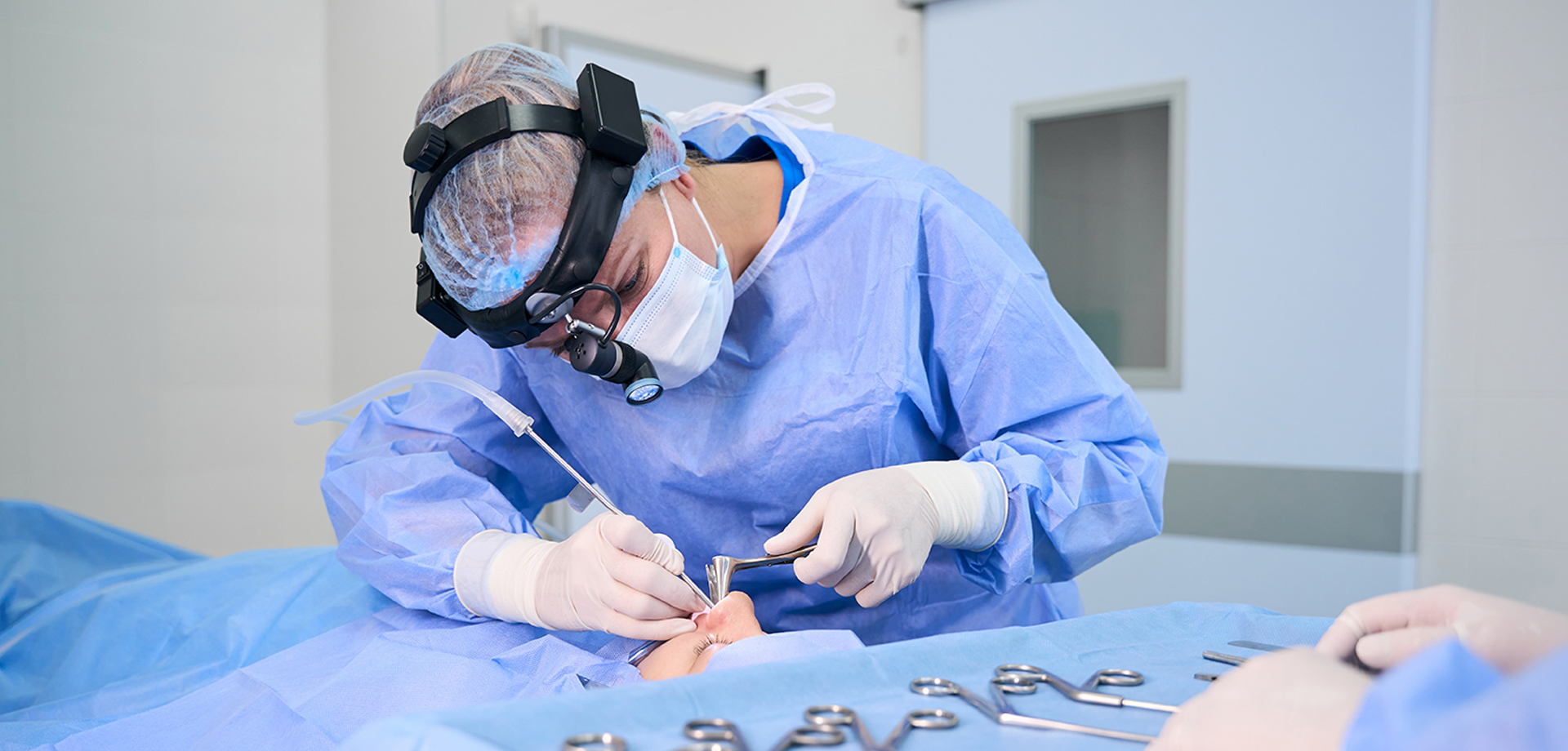
Balloon sinuplasty is a minimally invasive ENT procedure designed to treat selected cases of chronic and recurrent sinusitis by gently dilating narrowed sinus drainage pathways. Unlike traditional endoscopic sinus surgery, balloon sinuplasty does not involve removal of bone or soft tissue. Instead, it focuses on restoring normal sinus ventilation and drainage while preserving the natural anatomy of the nasal and sinus structures. Because of this tissue-sparing approach, balloon sinuplasty is associated with reduced postoperative discomfort, faster recovery, and minimal bleeding when appropriately indicated.
The paranasal sinuses drain mucus through small openings into the nasal cavity. In some patients, these drainage pathways become narrowed due to inflammation, scarring, or anatomical variation, leading to mucus retention, pressure buildup, and recurrent infections. Balloon sinuplasty is most effective in patients whose sinus symptoms are caused by isolated ostial obstruction rather than widespread sinus disease. It is not a universal replacement for conventional sinus surgery and requires careful patient selection by an ENT specialist.
Indications for balloon sinuplasty include chronic sinusitis or recurrent acute sinusitis that has not responded adequately to medical treatment such as antibiotics, nasal sprays, and allergy management. Patients typically experience facial pressure, nasal congestion, sinus headaches, and postnasal drip but do not have extensive nasal polyps, severe mucosal disease, or complex sinus anatomy. Preoperative evaluation includes nasal endoscopy and imaging, usually a CT scan of the sinuses, to confirm suitability for the procedure.
The balloon sinuplasty procedure is performed under endoscopic guidance, either under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia, depending on patient comfort and clinical setting. A flexible catheter with a deflated balloon is carefully advanced into the blocked sinus opening. Once positioned correctly, the balloon is gradually inflated to widen the sinus passage. This controlled dilation restructures the surrounding bone without cutting or removing tissue. After dilation, the balloon is deflated and removed, leaving the sinus opening enlarged to allow normal drainage and airflow.
One of the key advantages of balloon sinuplasty is its minimally invasive nature. There are no external incisions, and bleeding is minimal compared to traditional sinus surgery. Most patients experience mild nasal congestion or pressure for a short period after the procedure. Recovery is typically rapid, with many patients resuming normal daily activities within 24 to 48 hours. Postoperative care includes saline irrigation and continued medical management of underlying inflammation or allergies.
Clinical outcomes for balloon sinuplasty are favorable in appropriately selected patients. Many experience significant reduction in sinus symptoms, fewer infections, and improved quality of life. However, it is important to understand that balloon sinuplasty does not cure underlying inflammatory conditions. Long-term success depends on continued medical therapy, allergy control, and regular ENT follow-up.
Balloon sinuplasty is not suitable for all patients with sinus disease. Individuals with extensive nasal polyps, fungal sinusitis, severe chronic sinus inflammation, or complex anatomical disease typically benefit more from conventional endoscopic sinus surgery. An ENT specialist plays a critical role in determining the most effective and safe treatment option based on individual anatomy and disease severity.
When used in the right clinical context, balloon sinuplasty is a safe, effective, and patient-friendly option that bridges medical and surgical management of sinus disease.
The paranasal sinuses drain mucus through small openings into the nasal cavity. In some patients, these drainage pathways become narrowed due to inflammation, scarring, or anatomical variation, leading to mucus retention, pressure buildup, and recurrent infections. Balloon sinuplasty is most effective in patients whose sinus symptoms are caused by isolated ostial obstruction rather than widespread sinus disease. It is not a universal replacement for conventional sinus surgery and requires careful patient selection by an ENT specialist.
Indications for balloon sinuplasty include chronic sinusitis or recurrent acute sinusitis that has not responded adequately to medical treatment such as antibiotics, nasal sprays, and allergy management. Patients typically experience facial pressure, nasal congestion, sinus headaches, and postnasal drip but do not have extensive nasal polyps, severe mucosal disease, or complex sinus anatomy. Preoperative evaluation includes nasal endoscopy and imaging, usually a CT scan of the sinuses, to confirm suitability for the procedure.
The balloon sinuplasty procedure is performed under endoscopic guidance, either under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia, depending on patient comfort and clinical setting. A flexible catheter with a deflated balloon is carefully advanced into the blocked sinus opening. Once positioned correctly, the balloon is gradually inflated to widen the sinus passage. This controlled dilation restructures the surrounding bone without cutting or removing tissue. After dilation, the balloon is deflated and removed, leaving the sinus opening enlarged to allow normal drainage and airflow.
One of the key advantages of balloon sinuplasty is its minimally invasive nature. There are no external incisions, and bleeding is minimal compared to traditional sinus surgery. Most patients experience mild nasal congestion or pressure for a short period after the procedure. Recovery is typically rapid, with many patients resuming normal daily activities within 24 to 48 hours. Postoperative care includes saline irrigation and continued medical management of underlying inflammation or allergies.
Clinical outcomes for balloon sinuplasty are favorable in appropriately selected patients. Many experience significant reduction in sinus symptoms, fewer infections, and improved quality of life. However, it is important to understand that balloon sinuplasty does not cure underlying inflammatory conditions. Long-term success depends on continued medical therapy, allergy control, and regular ENT follow-up.
Balloon sinuplasty is not suitable for all patients with sinus disease. Individuals with extensive nasal polyps, fungal sinusitis, severe chronic sinus inflammation, or complex anatomical disease typically benefit more from conventional endoscopic sinus surgery. An ENT specialist plays a critical role in determining the most effective and safe treatment option based on individual anatomy and disease severity.
When used in the right clinical context, balloon sinuplasty is a safe, effective, and patient-friendly option that bridges medical and surgical management of sinus disease.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









