Advanced & Metabolic Procedures
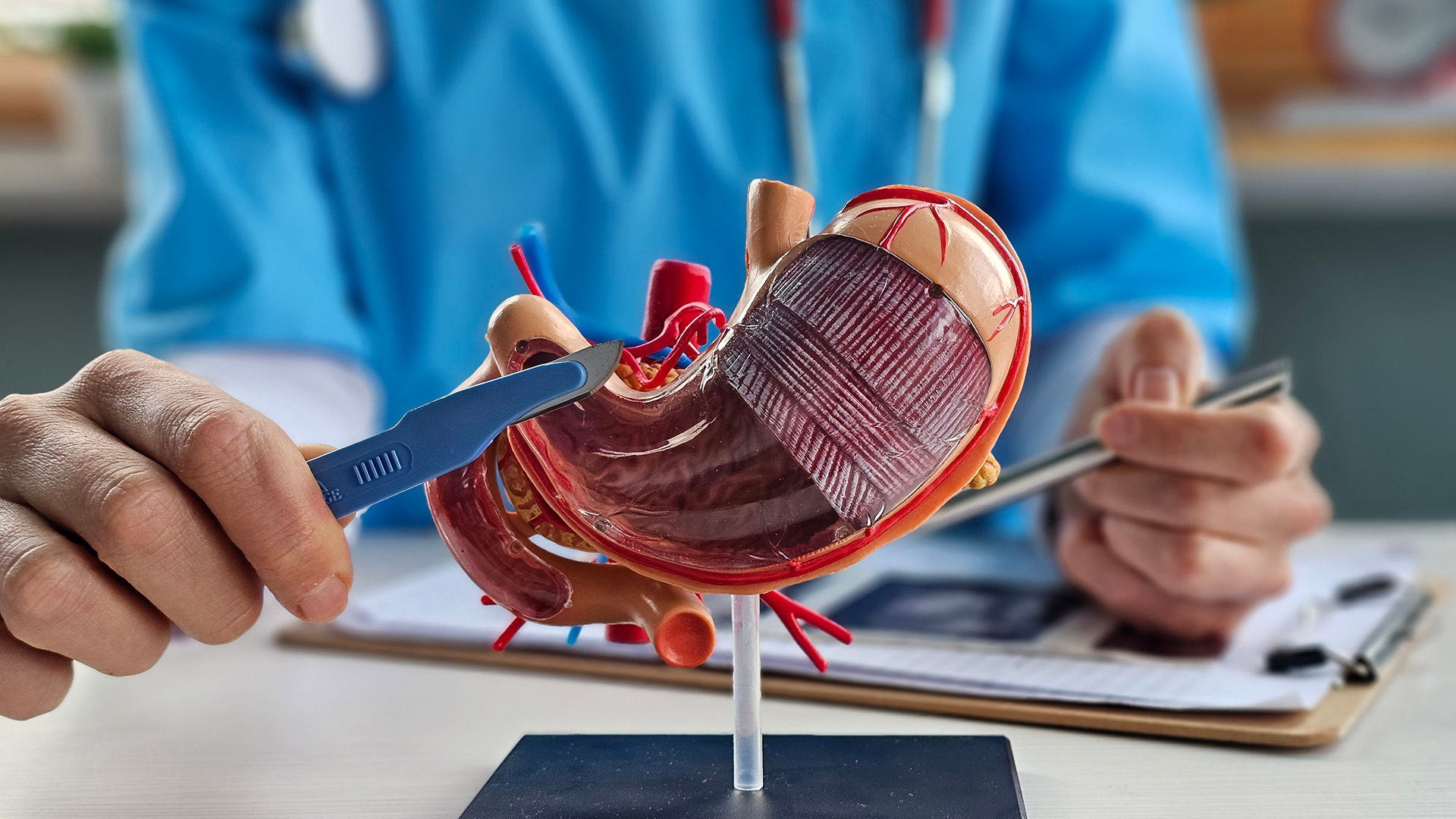
Mini Gastric Bypass, also known as One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB or MGB), is an advanced bariatric and metabolic surgery designed to deliver powerful and sustained weight loss while improving obesity-related metabolic conditions. It is increasingly favored due to its technical simplicity, strong metabolic outcomes, and shorter operative time when performed in appropriately selected patients.
The procedure involves creating a long, narrow stomach pouch similar to a sleeve and connecting it to a loop of the small intestine using a single intestinal connection (anastomosis). This configuration reduces stomach capacity and alters nutrient absorption, combining restrictive and malabsorptive mechanisms. By limiting food intake and reducing calorie absorption, OAGB promotes effective and durable weight loss.
One of the most significant advantages of mini gastric bypass is its profound metabolic impact. The procedure alters gut hormone signaling, leading to improved insulin sensitivity, appetite control, and glucose regulation. Many patients with obesity-related type 2 diabetes experience rapid improvement or remission of diabetes following surgery, often within weeks. This makes OAGB a strong option for patients seeking both weight loss and metabolic disease control.
Weight-loss outcomes with mini gastric bypass are comparable to or, in some cases, exceed those of traditional gastric bypass. Patients typically lose 65–80% of excess body weight within 12–18 months. Long-term studies demonstrate durable results when patients adhere to structured follow-up, nutritional guidance, and lifestyle modification.
The procedure is performed laparoscopically, using minimally invasive techniques that reduce surgical trauma, shorten hospital stay, and accelerate recovery. Most patients resume daily activities within a few weeks. The simplified surgical anatomy reduces operative time and may lower complication rates in experienced centers.
As with all bypass procedures, nutritional monitoring is essential. Because OAGB affects nutrient absorption, patients require lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation, including iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and fat-soluble vitamins. Regular follow-up ensures early detection and prevention of deficiencies.
Patient selection is critical. Pre-operative evaluation includes assessment of reflux symptoms, metabolic status, nutritional health, and long-term compliance potential. When performed within a multidisciplinary bariatric program, mini gastric bypass offers a safe, effective, and metabolically powerful solution for patients with obesity and related diseases.
The procedure involves creating a long, narrow stomach pouch similar to a sleeve and connecting it to a loop of the small intestine using a single intestinal connection (anastomosis). This configuration reduces stomach capacity and alters nutrient absorption, combining restrictive and malabsorptive mechanisms. By limiting food intake and reducing calorie absorption, OAGB promotes effective and durable weight loss.
One of the most significant advantages of mini gastric bypass is its profound metabolic impact. The procedure alters gut hormone signaling, leading to improved insulin sensitivity, appetite control, and glucose regulation. Many patients with obesity-related type 2 diabetes experience rapid improvement or remission of diabetes following surgery, often within weeks. This makes OAGB a strong option for patients seeking both weight loss and metabolic disease control.
Weight-loss outcomes with mini gastric bypass are comparable to or, in some cases, exceed those of traditional gastric bypass. Patients typically lose 65–80% of excess body weight within 12–18 months. Long-term studies demonstrate durable results when patients adhere to structured follow-up, nutritional guidance, and lifestyle modification.
The procedure is performed laparoscopically, using minimally invasive techniques that reduce surgical trauma, shorten hospital stay, and accelerate recovery. Most patients resume daily activities within a few weeks. The simplified surgical anatomy reduces operative time and may lower complication rates in experienced centers.
As with all bypass procedures, nutritional monitoring is essential. Because OAGB affects nutrient absorption, patients require lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation, including iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and fat-soluble vitamins. Regular follow-up ensures early detection and prevention of deficiencies.
Patient selection is critical. Pre-operative evaluation includes assessment of reflux symptoms, metabolic status, nutritional health, and long-term compliance potential. When performed within a multidisciplinary bariatric program, mini gastric bypass offers a safe, effective, and metabolically powerful solution for patients with obesity and related diseases.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









