Adenoidectomy
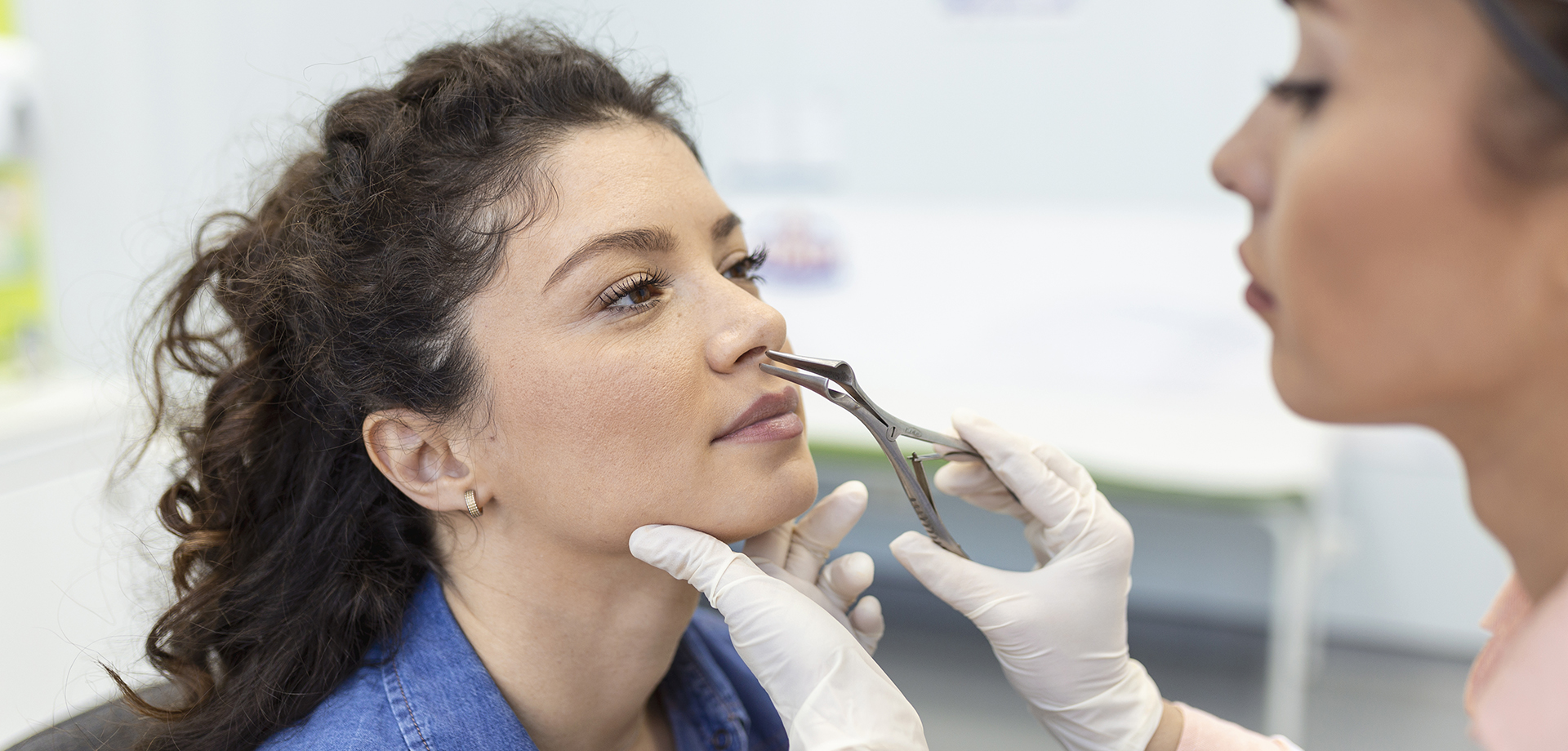
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure involving removal of the adenoids, which are lymphoid tissues located at the back of the nasal cavity above the roof of the mouth. Adenoids are part of the immune system and are most prominent in early childhood, gradually shrinking during adolescence. However, when adenoids become chronically enlarged or infected, they can cause significant nasal, ear, and sleep-related problems, particularly in children.
The most common indication for adenoidectomy is nasal airway obstruction due to adenoid hypertrophy. Enlarged adenoids can block airflow through the nasal passages, forcing children to breathe through the mouth. This leads to persistent mouth breathing, nasal speech, snoring, restless sleep, and daytime fatigue. In severe cases, adenoid hypertrophy contributes to obstructive sleep apnea, affecting growth, behavior, and cognitive development.
Recurrent or chronic ear infections are another major indication. Enlarged adenoids can obstruct the Eustachian tubes, impairing middle ear ventilation and leading to recurrent otitis media or persistent middle ear fluid. Children with repeated ear infections or hearing problems often benefit significantly from adenoid removal. Chronic sinusitis and recurrent nasal infections may also be associated with infected adenoidal tissue.
Adenoidectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia and is often combined with tonsillectomy or ear procedures when indicated. The surgeon accesses the adenoids through the mouth without external incisions. Specialized instruments or endoscopic guidance are used to remove the tissue safely while protecting surrounding structures. Bleeding control is achieved during the procedure, and surgery is usually completed within a short duration.
Recovery from adenoidectomy is generally rapid and well tolerated. Most children experience mild throat or nasal discomfort for a few days. Temporary nasal congestion or voice changes may occur but resolve as swelling subsides. Normal activities can usually be resumed within a few days, and long-term complications are rare.
Following adenoidectomy, children typically show marked improvement in nasal breathing, sleep quality, frequency of infections, and overall quality of life. ENT follow-up ensures proper recovery and monitors ear and nasal health post-surgery.
The most common indication for adenoidectomy is nasal airway obstruction due to adenoid hypertrophy. Enlarged adenoids can block airflow through the nasal passages, forcing children to breathe through the mouth. This leads to persistent mouth breathing, nasal speech, snoring, restless sleep, and daytime fatigue. In severe cases, adenoid hypertrophy contributes to obstructive sleep apnea, affecting growth, behavior, and cognitive development.
Recurrent or chronic ear infections are another major indication. Enlarged adenoids can obstruct the Eustachian tubes, impairing middle ear ventilation and leading to recurrent otitis media or persistent middle ear fluid. Children with repeated ear infections or hearing problems often benefit significantly from adenoid removal. Chronic sinusitis and recurrent nasal infections may also be associated with infected adenoidal tissue.
Adenoidectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia and is often combined with tonsillectomy or ear procedures when indicated. The surgeon accesses the adenoids through the mouth without external incisions. Specialized instruments or endoscopic guidance are used to remove the tissue safely while protecting surrounding structures. Bleeding control is achieved during the procedure, and surgery is usually completed within a short duration.
Recovery from adenoidectomy is generally rapid and well tolerated. Most children experience mild throat or nasal discomfort for a few days. Temporary nasal congestion or voice changes may occur but resolve as swelling subsides. Normal activities can usually be resumed within a few days, and long-term complications are rare.
Following adenoidectomy, children typically show marked improvement in nasal breathing, sleep quality, frequency of infections, and overall quality of life. ENT follow-up ensures proper recovery and monitors ear and nasal health post-surgery.
Quick Contact
If you have any questions simply use the following contact details.

Working Hours
-
Out-patient Department
Monday to Saturday 08:00 AM - 09:00 PM
Sunday 10:00 AM - 06:00 PM
-
Emergency Department & Pharmacy
Sunday to Saturday 24x7





 04 406 3000
04 406 3000  04 406 3000
04 406 3000









